Introduction: Benefits of Diversified ETF Investments in 2024
In the fast-paced world of investing, it’s essential to find strategies that not only promise potential returns but also mitigate risk effectively. Diversified ETF investment benefits are quickly becoming one of the most favored strategies among investors. As global markets continue to face uncertainty, the importance of having a diversified portfolio becomes increasingly evident. ETFs, or exchange-traded funds, offer an innovative solution that combines flexibility, affordability, and robust risk management. This article takes a deep dive into the benefits of investing in diversified ETFs, exploring how they can enhance your financial future and why they are a key asset for investors of all levels.
Understanding Diversified ETF Investment
At its core, diversified ETF investment revolves around one fundamental concept: reducing risk. Diversification spreads your investments across a wide range of asset classes—stocks, bonds, real estate, commodities, and even international markets—thereby decreasing the potential negative impact of any one investment. In contrast to traditional individual stock investments, where an investor’s money is tied to the performance of a single company, diversified ETFs allow for broader exposure across different sectors, industries, and even countries.
This strategy doesn’t just reduce risk, but also maximizes the opportunity for growth. By investing in an ETF, you gain exposure to a collection of stocks or assets that track major indices like the S&P 500, or more specific ones like emerging markets or sustainable technologies. Diversified ETFs essentially let you capture the collective growth potential of various sectors, thus improving your chances of a balanced, positive return on your investments.
The Top 5 Benefits of Diversified ETF Investments
1. Reduced Risk Through Diversification
Risk management is a critical element of any successful investment strategy. One of the primary diversified ETF investment benefits is the significant reduction in risk. Traditional investing in individual stocks can expose you to unpredictable fluctuations based on the performance of a single company. But when you invest in diversified ETFs, your risk is spread across hundreds or even thousands of assets, dramatically lowering the chances of a major loss.
For example, a diversified ETF like the Vanguard Total Stock Market ETF (VTI) offers exposure to the entire U.S. stock market, from small companies to large corporations across different sectors. This type of diversified ETF protects you from the volatility of individual stocks and gives you access to a broad range of industries. By holding a piece of many companies, sectors, and industries, you’re effectively hedging against the risk of any one entity’s poor performance.
Investing in a diversified ETF ensures that even if one or a few assets within the fund underperform, the rest of the investments within the ETF can potentially offset those losses, providing a safer investment environment.
2. Access to a Wide Range of Asset Classes
A significant advantage of diversified ETF investments is that they allow you to diversify across not just sectors, but different asset classes, including stocks, bonds, commodities, real estate, and even alternative investments. This versatility allows investors to create a robust, balanced portfolio with exposure to a variety of investment types, each providing different growth and risk profiles.
For example, the iShares MSCI Emerging Markets ETF (EEM) offers investors the opportunity to invest in fast-growing emerging markets like China, Brazil, and India, as well as various sectors, such as technology, healthcare, and finance. Diversified ETFs that track bonds or commodities such as gold and oil are also available, making it easy for you to access an even wider range of investment opportunities.
Furthermore, diversified ETFs like those that focus on global markets or multi-asset classes enable you to take advantage of opportunities in real estate (through REIT ETFs) or even socially responsible investing (SRI ETFs). This exposure to a range of asset classes ensures that your portfolio remains balanced, reducing the risk of relying too heavily on any single asset type or market sector.
3. Cost-Effective Investment Option
Investing in diversified ETFs is one of the most cost-effective ways to achieve broad exposure to multiple assets. Traditional mutual funds, which are actively managed, tend to carry higher management fees due to the fund managers’ decision-making processes. In contrast, ETFs are typically passively managed, tracking an index or a specific set of assets, and are often much cheaper to operate. This means that you, the investor, save on fees, allowing more of your capital to stay invested and generate returns.
For instance, the expense ratio for the Vanguard Total Stock Market ETF (VTI) is only 0.03%, which is significantly lower than the average mutual fund expense ratio of around 0.75% to 1.5%. This cost-efficiency makes ETFs particularly appealing to long-term investors who want to minimize fees and maximize their investment returns.
By avoiding high management fees and transactional costs associated with individual stock trading or actively managed funds, ETFs provide a simple and affordable way for investors to diversify and stay invested in the markets.
4. Liquidity and Flexibility
Liquidity is a crucial consideration for any investor, and ETFs offer exceptional flexibility in this area. Unlike mutual funds, which are only priced and traded at the end of the trading day, ETFs are traded throughout the day on the stock exchange. This means that you can buy or sell your ETF shares at any time during market hours, just like individual stocks.
The liquidity of ETFs makes it easier to adjust your portfolio as market conditions change, providing you with the flexibility to react to news or events that may affect specific sectors or industries. For instance, if there is a downturn in technology stocks, you can easily sell your technology ETF shares and reallocate funds into another sector or asset class that might be performing better. This liquidity also provides an added level of control over your investments, allowing you to execute trades when the market conditions are right for you.
Moreover, ETFs allow you to pursue a wide variety of investment strategies. Whether you’re interested in growth investing, dividend investing, or sector rotation, ETFs provide the flexibility to tailor your portfolio to match your specific financial goals.
5. Transparency and Simplicity
One of the standout features of ETFs is their transparency. Most ETF providers publish their holdings on a daily basis, which means that you can always see which assets are part of the ETF and track their performance in real time. This level of transparency is not always available with other investment products, such as mutual funds, which typically disclose their holdings quarterly.
For instance, the SPDR S&P 500 ETF (SPY) holds stocks from the 500 largest publicly traded companies in the U.S. You can easily find detailed information about the specific stocks included in the fund and monitor their performance to ensure that the ETF continues to align with your investment objectives. This transparency not only provides peace of mind but also enables you to adjust your portfolio if necessary.
Additionally, ETFs are relatively easy to understand, even for novice investors. You don’t need to be a financial expert to recognize the value of a diversified investment that tracks an index or a specific sector. Whether you’re just starting out or are an experienced investor, ETFs provide a straightforward and accessible way to invest in a broad range of assets.
Real-Life Examples of Diversified ETFs
1. Vanguard Total Stock Market ETF (VTI)
The Vanguard Total Stock Market ETF is a great example of a diversified ETF, providing exposure to the entire U.S. stock market. VTI tracks the performance of the CRSP US Total Market Index, which includes stocks from large, mid, small, and micro-cap companies in various sectors, including technology, healthcare, and consumer goods.
You can find more information about the Vanguard Total Stock Market ETF here: VTI – Vanguard Total Stock Market ETF.
2. iShares MSCI Emerging Markets ETF (EEM)
EEM offers exposure to companies in emerging markets like China, Brazil, India, and South Africa. This ETF gives investors access to high-growth regions, balancing potential risks with the opportunity for higher returns.
For more details on the iShares MSCI Emerging Markets ETF, visit: EEM – iShares MSCI Emerging Markets ETF.
3. SPDR S&P 500 ETF (SPY)
The SPY ETF is one of the most widely known and traded ETFs, which tracks the performance of the S&P 500 index. It offers exposure to the 500 largest publicly traded U.S. companies across all sectors, including technology, healthcare, and financials.
For further information on the SPDR S&P 500 ETF, check out: SPY – SPDR S&P 500 ETF.
The Timeline of Growth in ETF Investments
The growth of ETFs began in the early 1990s, with the launch of the first exchange-traded fund, the SPDR S&P 500 ETF (SPY), in January 1993. The launch of this ETF was a significant milestone in the history of financial markets, as it allowed investors to gain exposure to the S&P 500 index in a single transaction.
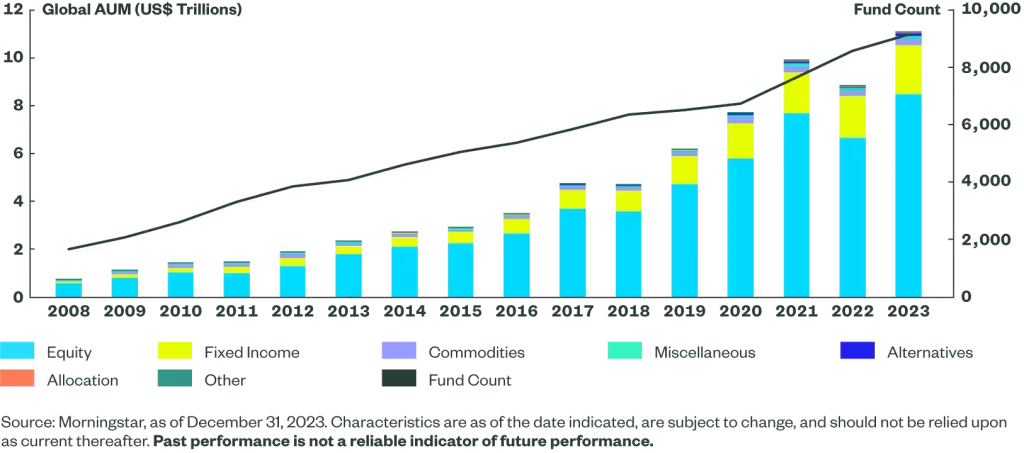
Over the next two decades, ETFs began to evolve, and more specialized ETFs began to appear, providing exposure to sectors such as technology, healthcare, and energy, as well as international markets and commodities. By 2010, global ETF assets had reached over $1 trillion, and today, the ETF market is valued at over $10 trillion. The surge in popularity is due to the increasing demand for low-cost, diversified investment options, with many investors preferring passive strategies over actively managed funds.
The rise of thematic ETFs and ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) ETFs in recent years marks a shift toward more personalized and sustainable investment options. These ETFs allow investors to align their investments with specific values or interests, such as renewable energy, social justice, or gender diversity.
Expert Opinions
- John Bogle, founder of Vanguard Group, was a strong advocate for index investing and the power of diversification through ETFs. Bogle stated, “The more you diversify, the better chance you have of winning.” His philosophy of low-cost, broad diversification has had a lasting impact on the ETF industry and continues to shape investment strategies today.
- Nassim Nicholas Taleb, author of The Black Swan, emphasizes the importance of risk management and diversification in investing. He notes, “You should never put all your eggs in one basket.” Taleb’s insight highlights the need for diversified ETF investment to reduce the risks associated with volatile markets.
Conclusion: Why You Should Consider Diversified ETF Investments
In conclusion, the diversified ETF investment benefits are clear: they provide reduced risk, access to a wide range of asset classes, cost-effectiveness, liquidity, and transparency. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced investor, diversified ETFs offer a reliable way to achieve a balanced and resilient portfolio. With the flexibility to invest across sectors, industries, and regions, ETFs enable you to tap into a wealth of growth opportunities while minimizing the impact of risk.
As we look to the future, ETFs will continue to evolve, offering even more tailored options for investors seeking to diversify their portfolios. By leveraging these investment vehicles, you can set yourself up for long-term financial success and peace of mind.
 Take Your Trading And Financial Skills to the Next Level!
Take Your Trading And Financial Skills to the Next Level!
If you enjoyed this post, dive deeper with our Profitable Trader Series—a step-by-step guide to mastering the stock market.
- Stock Market 101: Profits with Candlesticks
- Stock Market 201: Profits with Chart Patterns
- Stock Market 301: Advanced Trade Sheets
Start your journey now!
For Regular Finance Updates Follow – Daily Business
FAQs
Q1: What is the difference between ETFs and mutual funds?
- Answer: ETFs (Exchange-Traded Funds) are investment funds that trade on stock exchanges, similar to individual stocks. They offer lower fees, are more flexible, and are traded throughout the day. Mutual funds, on the other hand, are managed by professional fund managers and typically only trade at the end of the day, often carrying higher management fees.
Q2: Are diversified ETFs safer than individual stock investments?
- Answer: Yes, diversified ETFs are typically safer than investing in individual stocks because they spread your investment across a broad range of companies, sectors, or asset classes, reducing the impact of any one company’s poor performance. This diversification minimizes risk and provides more stable returns.
Q3: Can I invest in ETFs through a retirement account?
- Answer: Yes, you can invest in ETFs through retirement accounts like IRAs and 401(k)s. Many brokerage firms allow investors to buy and sell ETFs within these tax-advantaged accounts, providing an opportunity for long-term growth.
Q4: How do I choose the best diversified ETF for my portfolio?
- Answer: The best diversified ETF for your portfolio depends on your financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment timeline. Start by researching ETFs that track major indices or sectors you believe will perform well. Consider factors like expense ratios, past performance, and the types of assets the ETF holds.
Q5: Are there ETFs that focus on sustainable and socially responsible investing?
- Answer: Yes, there are ETFs that focus on socially responsible investing (SRI), environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria. These ETFs invest in companies that meet specific sustainability or ethical standards, making them an appealing choice for socially conscious investors.