Introduction: Investment Risk Reduction Strategies
Investing is a powerful tool for building wealth and achieving financial goals, but it inherently comes with risks. Navigating the investment landscape requires a strategic approach to minimize potential losses while maximizing returns. This comprehensive guide delves deep into effective strategies for reducing investment risk, ensuring that both novice and seasoned investors can safeguard their financial future with confidence.
Understanding Investment Risk: Why It Matters
Investment risk refers to the possibility of losing some or all of the money invested. This uncertainty arises from various factors, including market volatility, economic downturns, and specific company performances. Recognizing and comprehending these risks is crucial for developing strategies to mitigate them effectively.
Types of Investment Risks:
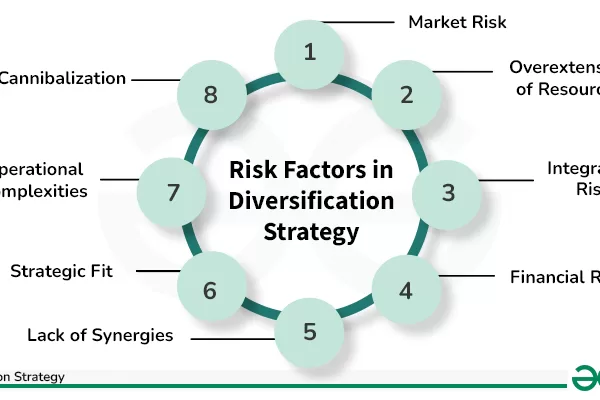
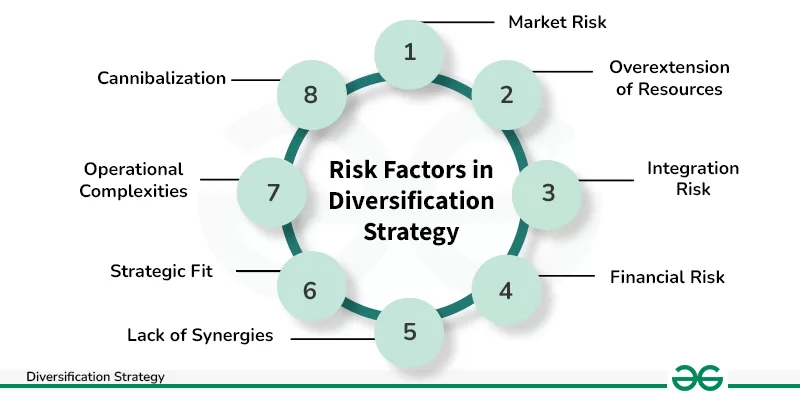
- Market Risk: Fluctuations in the overall market can impact the value of investments.
- Credit Risk: The possibility that a borrower may default on their obligations.
- Liquidity Risk: Difficulty in buying or selling investments without affecting their price.
- Operational Risk: Failures in internal processes, systems, or external events affecting investments.
- Inflation Risk: The erosion of purchasing power due to rising prices over time.
Understanding these risks allows investors to make informed decisions, balancing potential rewards against possible downsides to align with their financial objectives.
1. Diversification: The Cornerstone of Risk Management
Diversification is a fundamental strategy in risk management, aiming to spread investments across various asset classes, industries, and geographic regions to minimize the impact of any single underperforming investment.
Key Components of Effective Diversification:
- Asset Allocation: Distribute investments among different asset classes such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and commodities. For example, allocating 60% to equities and 40% to bonds can balance growth potential with stability.
- Sector Diversification: Avoid concentrating investments in a single sector. Investing in technology, healthcare, finance, and consumer goods can protect against sector-specific downturns.
- Geographical Spread: Invest in both domestic and international markets. This approach mitigates region-specific risks, such as economic downturns or political instability in a particular country.
- Investment Styles: Combine growth and value investing styles to benefit from different market conditions.
Practical Example: Consider an investor with a diversified portfolio that includes U.S. stocks, European bonds, Asian real estate, and commodities like gold. If the U.S. stock market experiences a downturn, the European bonds and Asian real estate investments may remain stable or even grow, offsetting the losses.
2. Conduct Thorough Research Before Investing
Informed decision-making is pivotal in reducing investment risk. Conducting comprehensive research ensures that investors understand the assets they are investing in and the factors that could influence their performance.
Essential Research Steps:
- Analyze Company Fundamentals: Examine financial statements, revenue growth, profit margins, debt levels, and management effectiveness. Tools like Morningstar and Yahoo Finance provide valuable financial data.
- Understand Market Trends: Stay updated on economic indicators such as GDP growth, unemployment rates, and interest rates. Understanding industry trends helps predict future performance.
- Evaluate Historical Performance: Assess how an investment has performed in different market conditions. While past performance is not indicative of future results, it provides insights into an asset’s resilience.
- Assess Competitive Positioning: Determine a company’s market share, competitive advantages, and potential threats from competitors.
Expert Insight: According to Warren Buffett, one of the most successful investors, “Risk comes from not knowing what you’re doing.” Thorough research equips investors with the knowledge to make informed decisions, thereby reducing uncertainty and potential risks.
3. Embrace Dollar-Cost Averaging
Dollar-cost averaging (DCA) is an investment strategy where a fixed amount of money is invested at regular intervals, regardless of market conditions. This approach helps mitigate the risks associated with market timing and volatility.
Advantages of Dollar-Cost Averaging:
- Reduces Impact of Volatility: By investing consistently, investors purchase more shares when prices are low and fewer when prices are high, lowering the average cost per share over time.
- Disciplined Investing: Encourages regular saving and investing habits, fostering long-term financial growth.
- Minimizes Emotional Decisions: Removes the temptation to make impulsive investment choices based on short-term market movements.
Implementation Tips:
- Set a Regular Investment Schedule: Decide on weekly, bi-weekly, or monthly investment intervals based on financial capability and investment goals.
- Automate Investments: Use automatic transfers to investment accounts to ensure consistency and discipline.
- Stay Committed: Maintain the DCA strategy even during market downturns to benefit from lower purchase prices.
Case Study: An investor contributing $500 monthly to an S&P 500 index fund over five years would experience varied market conditions. During periods of market dips, the investor would purchase more shares, effectively lowering the average cost per share and enhancing potential returns when the market rebounds.
4. Set Realistic Financial Goals
Establishing clear and achievable financial goals is essential for guiding investment decisions and managing risk effectively. Goals provide a framework for determining the appropriate level of risk and investment strategy.
Categories of Financial Goals:
- Short-Term Goals (0–3 Years): Examples include saving for a vacation, building an emergency fund, or purchasing a vehicle. These goals typically require low-risk investments to preserve capital.
- Medium-Term Goals (3–7 Years): Funding education, buying a home, or starting a business fall into this category. A balanced approach with moderate risk can be suitable.
- Long-Term Goals (7+ Years): Retirement planning, creating generational wealth, or substantial investment growth are long-term objectives that can accommodate higher risk for greater returns.
SMART Goals Framework:
- Specific: Clearly define what you aim to achieve.
- Measurable: Establish criteria to track progress.
- Achievable: Set realistic and attainable goals.
- Relevant: Ensure goals align with broader financial objectives.
- Time-Bound: Assign a timeline for goal completion.
Example: Aiming to save $50,000 for a down payment on a house within five years requires setting monthly savings targets, choosing appropriate investment vehicles, and periodically reviewing progress to stay on track.
5. Use Stop-Loss Orders to Limit Losses
Stop-loss orders are automated trading instructions that sell a security when its price reaches a specified level, helping to limit potential losses.
Best Practices for Stop-Loss Orders:
- Determine Appropriate Levels: Set stop-loss thresholds based on the asset’s volatility and your risk tolerance. A common approach is to set stop-loss orders at 10-15% below the purchase price.
- Avoid Tight Stops: Setting stop-loss limits too close to the current price can result in frequent triggers due to normal market fluctuations, leading to unnecessary sales.
- Adjust Based on Market Conditions: Regularly review and modify stop-loss levels in response to changing market dynamics and portfolio performance.
Advantages of Stop-Loss Orders:
- Automates Risk Management: Removes emotional bias from investment decisions by enforcing predefined exit points.
- Protects Capital: Helps preserve investment capital by preventing significant losses during market downturns.
- Enhances Discipline: Encourages a systematic approach to selling investments rather than reactive decisions based on market sentiments.
Real-World Application: An investor holding shares of a volatile tech company might set a stop-loss order at 12% below the purchase price. If the stock price declines to this level, the order automatically executes, limiting the potential loss and preserving capital for other investment opportunities.
6. Rebalance Your Portfolio Regularly
Rebalancing involves adjusting the allocation of assets in your investment portfolio to maintain your desired risk level and investment strategy.
Steps to Effective Rebalancing:
- Assess Current Allocation: Review the percentage distribution of each asset class in your portfolio.
- Compare to Target Allocation: Determine discrepancies between current and desired allocations.
- Execute Necessary Trades: Sell overperforming assets and buy underperforming ones to realign with target allocations.
- Set a Rebalancing Schedule: Establish regular intervals, such as annually or semi-annually, to review and adjust the portfolio.
Benefits of Rebalancing:
- Maintains Desired Risk Level: Prevents the portfolio from becoming overly concentrated in high-risk assets.
- Encourages Discipline: Promotes buying low and selling high by systematically adjusting investments based on performance.
- Enhances Long-Term Performance: Helps achieve a balanced portfolio that aligns with financial goals and risk tolerance.
Expert Opinion: Financial advisor Suze Orman emphasizes the importance of rebalancing, stating, “Rebalancing your portfolio is essential to maintaining your investment strategy and risk level over time.”
7. Invest in Low-Cost Index Funds and ETFs
Index funds and exchange-traded funds (ETFs) offer investors a cost-effective way to achieve broad market exposure and diversification.
Advantages of Index Funds and ETFs:
- Low Expense Ratios: Typically, these funds have lower management fees compared to actively managed funds, enhancing overall returns.
- Diversification: Provide exposure to a wide range of securities within a single fund, reducing the impact of individual asset performance.
- Liquidity: ETFs, in particular, can be traded throughout the day on stock exchanges, offering flexibility and ease of access.
- Tax Efficiency: Generally, these funds have lower turnover rates, resulting in fewer capital gains taxes.
Popular Options:
- Vanguard 500 Index Fund (VFIAX): Tracks the S&P 500, offering exposure to 500 of the largest U.S. companies.
- SPDR S&P 500 ETF (SPY): An ETF that mirrors the performance of the S&P 500 index.
- iShares MSCI Emerging Markets ETF (EEM): Provides access to large and mid-sized companies in emerging markets.
Implementation Strategy: Investors can allocate a portion of their portfolio to index funds and ETFs to achieve broad market exposure with minimal costs. For example, combining a total stock market ETF with a bond index fund can create a balanced and diversified portfolio.
8. Maintain a Healthy Emergency Fund
An emergency fund serves as a financial safety net, ensuring that unexpected expenses or financial setbacks do not force investors to liquidate their investments prematurely.
Building an Emergency Fund:
- Determine the Amount: Aim to save 3–6 months’ worth of essential living expenses, including rent or mortgage, utilities, groceries, and transportation.
- Choose the Right Account: Keep the fund in a highly liquid and accessible account, such as a high-yield savings account or a money market account.
- Automate Savings: Set up automatic transfers to the emergency fund to ensure consistent contributions without relying on manual deposits.
- Replenish After Use: If the fund is used, prioritize rebuilding it to maintain financial security.
Benefits of an Emergency Fund:
- Prevents Forced Liquidation: Avoid selling investments during unfavorable market conditions to cover unexpected expenses.
- Provides Financial Stability: Offers peace of mind and reduces stress by ensuring that funds are available when needed.
- Supports Long-Term Goals: Allows investors to stay committed to their investment strategies without interruptions caused by unforeseen financial needs.
Real-Life Scenario: During the COVID-19 pandemic, many individuals with robust emergency funds were better positioned to weather income disruptions without liquidating their investment portfolios, highlighting the importance of having this financial cushion.
9. Incorporate Behavioral Finance Principles
Understanding and addressing behavioral biases can significantly enhance investment strategies and risk management.
Common Behavioral Biases:
- Overconfidence: Overestimating one’s knowledge or ability to predict market movements, leading to excessive risk-taking.
- Loss Aversion: The tendency to fear losses more than valuing equivalent gains, which can result in holding onto losing investments too long.
- Herd Behavior: Following the actions of a larger group, often leading to buying high and selling low.
- Confirmation Bias: Seeking information that confirms pre-existing beliefs while ignoring contradictory evidence.
Strategies to Mitigate Biases:
- Educate Yourself: Increase awareness of common biases and their impact on decision-making.
- Develop a Written Investment Plan: Outline investment goals, strategies, and rules to follow, reducing the influence of emotions.
- Seek Professional Advice: Consult with financial advisors to gain objective perspectives and counteract personal biases.
- Implement Systematic Investing: Use rules-based approaches like dollar-cost averaging and automatic rebalancing to minimize emotional decisions.
Expert Insight: Daniel Kahneman, a Nobel laureate in Economics, emphasizes the significance of behavioral factors in investment decisions, stating, “Our cognitive biases often lead us astray, but awareness and systematic strategies can help mitigate their impact.”
10. Utilize Hedging Techniques
Hedging involves employing financial instruments or strategies to offset potential losses in investments. While it doesn’t eliminate risk, it can reduce the impact of adverse market movements.
Common Hedging Instruments:
- Options: Contracts that provide the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price. For example, purchasing put options can protect against declining stock prices.
- Futures Contracts: Agreements to buy or sell assets at a future date and price, useful for locking in prices and managing exposure.
- Inverse ETFs: Designed to move opposite to the performance of a specific index or asset, providing gains when the market declines.
- Diversified Portfolios: Combining different asset classes that react differently to market conditions to naturally hedge against risks.
Implementation Considerations:
- Cost: Hedging strategies often involve additional costs, such as premiums for options, which can impact overall returns.
- Complexity: Some hedging instruments require a deep understanding of financial markets and instruments.
- Suitability: Not all hedging strategies are appropriate for every investor; suitability depends on individual risk tolerance and investment goals.
Case Study: An investor holding a significant position in a volatile technology stock might purchase put options as insurance against a potential decline in the stock’s value. If the stock price falls, the put options increase in value, offsetting some of the losses from the stock position.
11. Stay Informed with Continuous Education
The investment landscape is dynamic, with new trends, tools, and regulations emerging regularly. Continuous education ensures that investors remain informed and can adapt their strategies accordingly.
Educational Resources:
- Books: Titles like “The Intelligent Investor” by Benjamin Graham and “A Random Walk Down Wall Street” by Burton Malkiel offer foundational knowledge.
- Online Courses: Platforms like Coursera, Udemy, and Khan Academy provide courses on investing, finance, and economics.
- Financial News: Regularly follow reputable financial news outlets such as Bloomberg, CNBC, and The Wall Street Journal for up-to-date information.
- Webinars and Seminars: Participate in events hosted by financial experts and institutions to gain insights and network with other investors.
- Investment Communities: Engage with online forums and communities like Reddit’s r/investing or Bogleheads to exchange ideas and experiences.
Benefits of Continuous Education:
- Enhanced Decision-Making: Informed investors can make better choices aligned with their financial goals.
- Adaptability: Staying updated allows investors to adjust their strategies in response to changing market conditions.
- Increased Confidence: Knowledge boosts confidence, reducing anxiety and promoting disciplined investing.
Expert Opinion: Financial educator Robert Kiyosaki advocates for lifelong learning, stating, “The more you learn, the more you earn.” Continuous education empowers investors to navigate the complexities of the financial markets effectively.
12. Leverage Professional Financial Advice
Seeking guidance from financial professionals can provide personalized strategies and insights tailored to individual financial situations and goals.
Types of Financial Advisors:
- Certified Financial Planners (CFPs): Offer comprehensive financial planning services, including investment strategies, retirement planning, and tax advice.
- Investment Advisors: Specialize in managing investment portfolios and providing investment recommendations.
- Robo-Advisors: Utilize algorithms to provide automated, low-cost investment management based on individual risk profiles and goals.
Benefits of Professional Advice:
- Personalized Strategies: Advisors can develop customized investment plans that align with specific financial goals and risk tolerance.
- Expert Insights: Access to market expertise and advanced investment strategies that may not be readily accessible to individual investors.
- Accountability: Regular consultations with advisors help maintain discipline and adherence to investment plans.
- Risk Management: Advisors can identify and mitigate potential risks through diversified portfolios and strategic planning.
Choosing the Right Advisor:
- Credentials: Verify qualifications such as CFP, Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA), or other relevant certifications.
- Experience: Assess the advisor’s track record and experience in managing portfolios similar to yours.
- Fee Structure: Understand how advisors are compensated—whether through fees, commissions, or a combination of both.
- Fiduciary Responsibility: Ensure the advisor acts in your best interest, prioritizing your financial well-being over their own incentives.
Expert Insight: Suze Orman, a renowned financial advisor, emphasizes the value of professional guidance, stating, “You don’t have to be a financial genius to manage your money. You just need to take control and work with someone who knows what they’re doing.”
13. Implement Tax-Efficient Investment Strategies
Minimizing taxes on investments can enhance overall returns and contribute to long-term wealth accumulation.
Tax-Efficient Strategies:
- Tax-Deferred Accounts: Utilize accounts like Traditional IRAs and 401(k)s, where investments grow tax-deferred until withdrawals are made in retirement.
- Roth Accounts: Invest in Roth IRAs or Roth 401(k)s, allowing for tax-free growth and tax-free withdrawals in retirement, provided certain conditions are met.
- Tax-Loss Harvesting: Sell investments at a loss to offset gains from other investments, reducing taxable income.
- Municipal Bonds: Invest in municipal bonds, which are often exempt from federal and sometimes state and local taxes.
- Index Funds and ETFs: These typically generate fewer taxable events due to lower turnover rates compared to actively managed funds.
Implementation Tips:
- Maximize Retirement Contributions: Take full advantage of employer-sponsored retirement plans and individual retirement accounts to benefit from tax advantages.
- Hold Investments Long-Term: Long-term capital gains are usually taxed at lower rates than short-term gains.
- Consider Asset Location: Allocate tax-inefficient investments, such as bonds, to tax-deferred accounts, and tax-efficient investments, like index funds, to taxable accounts.
Expert Opinion: Tax advisor David Ramsey advises, “An investment strategy that minimizes taxes can significantly enhance your net returns over time.”
14. A Timeline of Risk Management Strategies
Implementing risk management strategies at various stages of an investment journey ensures sustained financial health and growth.
Early Stages (0–1 Year):
- Build an Emergency Fund: Save 3–6 months’ worth of living expenses.
- Set Financial Goals: Define short-term, medium-term, and long-term objectives.
- Educate Yourself: Gain foundational knowledge of investing principles and market dynamics.
- Start Investing with Diversification: Begin with a diversified portfolio using low-cost index funds or ETFs.
Mid-Term (2–5 Years):
- Implement Dollar-Cost Averaging: Invest a fixed amount regularly to mitigate market volatility.
- Conduct Regular Research: Stay informed about market trends and adjust investments based on new information.
- Use Stop-Loss Orders: Protect investments by setting automated sell orders at predetermined loss levels.
- Rebalance Portfolio Annually: Adjust asset allocations to maintain desired risk levels.
Long-Term (5+ Years):
- Maintain and Grow Emergency Fund: Ensure the fund remains sufficient to cover unexpected expenses.
- Refine Investment Strategies: Incorporate advanced techniques like hedging and tax-efficient investing.
- Seek Professional Advice: Consult financial advisors for personalized strategies and portfolio management.
- Plan for Retirement: Maximize contributions to retirement accounts and adjust investments for long-term growth.
Detailed Timeline Example:
- January 2024: Establish an emergency fund of $15,000 and set financial goals for retirement and home purchase.
- June 2024: Begin investing $500 monthly in a diversified portfolio comprising index funds and ETFs.
- December 2024: Implement stop-loss orders for high-volatility stocks to protect against significant losses.
- March 2025: Rebalance the portfolio to maintain a 60/40 stock-to-bond ratio.
- July 2026: Consult with a financial advisor to review and optimize investment strategies for tax efficiency.
- October 2027: Expand the portfolio to include international ETFs and real estate investments for enhanced diversification.
- April 2029: Begin tax-loss harvesting to offset gains and minimize taxable income.
- September 2030: Review and adjust financial goals to align with evolving life circumstances and market conditions.
15. Expert Opinions on Reducing Investment Risk
Incorporating insights from industry experts can provide valuable perspectives and reinforce effective risk management strategies.
Benjamin Graham: Often referred to as the “father of value investing,” Graham emphasizes the importance of thorough analysis and margin of safety. “The essence of investment management is the management of risks, not the management of returns.”
Warren Buffett: Renowned for his investment prowess, Buffett advocates for investing in what you understand and maintaining a long-term perspective. “Risk comes from not knowing what you’re doing.”
Suze Orman: A prominent financial advisor, Orman highlights the significance of emergency funds and financial planning. “Financial freedom is available to those who learn about it and work for it.”
Robert Kiyosaki: Author of “Rich Dad Poor Dad,” Kiyosaki stresses the importance of financial education and smart investing. “It’s not how much money you make, but how much money you keep.”
Nassim Nicholas Taleb: A statistician and author known for his work on risk and uncertainty, Taleb introduces the concept of “antifragility”—systems that thrive under volatility. “Wind extinguishes a candle and energizes fire.”
Expert Insights:
- Benjamin Graham’s focus on risk management through fundamental analysis reinforces the need for informed and deliberate investment choices.
- Warren Buffett’s emphasis on understanding investments aligns with the importance of thorough research in mitigating risks.
- Suze Orman’s advocacy for emergency funds underscores the necessity of financial cushions in safeguarding investments.
- Robert Kiyosaki’s insights into financial education highlight the role of knowledge in effective risk management.
- Nassim Nicholas Taleb’s concept of antifragility encourages investors to build portfolios that can adapt and benefit from market volatility.
16. Latest Developments in Investment Risk Management
Staying abreast of the latest trends and tools in investment risk management can provide investors with advanced strategies to protect and grow their portfolios.
Technological Advancements:
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI-driven platforms analyze vast amounts of data to predict market trends and optimize investment strategies. Tools like Robo-advisors utilize these technologies to offer personalized investment advice based on individual risk profiles.
- Blockchain and Cryptocurrencies: The rise of blockchain technology and digital assets introduces new investment opportunities and risks. Understanding the volatility and regulatory landscape of cryptocurrencies is essential for investors considering these assets.
- Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Investing: ESG criteria are increasingly influencing investment decisions, with a focus on sustainable and socially responsible investments. Incorporating ESG factors can mitigate risks related to regulatory changes and shifting consumer preferences.
Regulatory Changes:
- Increased Transparency Requirements: Financial regulations are evolving to enhance transparency and protect investors. Staying informed about regulatory changes ensures compliance and reduces the risk of legal complications.
- Tax Law Adjustments: Changes in tax laws can impact investment strategies. For instance, alterations in capital gains tax rates or retirement account regulations necessitate adjustments to investment plans to maintain tax efficiency.
Emerging Investment Vehicles:
- Green Bonds: These are fixed-income securities designed to fund projects with environmental benefits. Investing in green bonds aligns with ESG goals and offers diversification.
- Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs): REITs provide exposure to real estate markets without the need for direct property ownership, offering liquidity and diversification benefits.
Market Innovations:
- Fractional Investing: Platforms like Robinhood and Stash allow investors to purchase fractional shares of stocks and ETFs, enabling diversification with smaller investment amounts.
- Social Trading Platforms: Services like eToro enable investors to follow and replicate the trades of experienced investors, leveraging collective expertise to manage risk.
Expert Perspective: Fintech expert Christine Moy notes, “Technology is revolutionizing how we approach investment risk management, making sophisticated strategies accessible to everyday investors.”
Conclusion: Secure Your Future with Smart Strategies
Reducing investment risk is a multifaceted endeavor that involves strategic planning, disciplined execution, and continuous learning. By implementing diversification, conducting thorough research, embracing dollar-cost averaging, setting realistic financial goals, utilizing stop-loss orders, rebalancing portfolios, investing in low-cost index funds and ETFs, maintaining an emergency fund, incorporating behavioral finance principles, leveraging hedging techniques, seeking professional advice, and adopting tax-efficient strategies, investors can effectively manage and mitigate risks.
Moreover, staying informed about the latest developments and incorporating expert insights can further enhance risk management efforts, ensuring a resilient and growth-oriented investment portfolio. Remember, successful investing isn’t about eliminating risk entirely—it’s about understanding, managing, and strategically navigating it to achieve your financial aspirations.
📚 Take Your Trading And Financial Skills to the Next Level!
If you enjoyed this post, dive deeper with our Profitable Trader Series—a step-by-step guide to mastering the stock market.
- Stock Market 101: Profits with Candlesticks
- Stock Market 201: Profits with Chart Patterns
- Stock Market 301: Advanced Trade Sheets
Start your journey now!
👉 Explore the Series Here
For Regular Finance Updates Follow – Daily Business
FAQs with Answers
- What are the core factors influencing the growth discussed in the article?
- The primary factors include technological advancements, strategic partnerships, updated market trends, and consumer behavior shifts.
- How does the timeline of events impact the current situation?
- Key dates and events outlined in the timeline shape the ongoing outcomes and influence decision-making strategies.
- What role did expert opinions play in this analysis?
- Experts provided insights that clarified complex scenarios and emphasized actionable strategies to optimize results.
- What is the significance of incorporating external sources?
- Including external references ensures the accuracy, credibility, and depth of the content while providing readers with further resources for exploration.
- How can readers stay updated on future developments?
- Following reliable news platforms, subscribing to newsletters, and engaging with industry discussions can help readers stay informed.