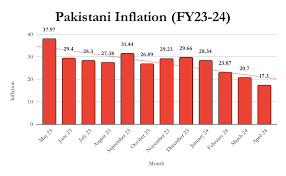
Pakistan inflation rate fell to 23.1% in February 2024, marking the lowest level since mid-2022. This detailed analysis explores the timeline leading to this significant decline, expert opinions, and the broader economic implications.
Timeline of Key Economic Events
June 2022: Pakistan’s inflation reached a peak of 27.6%, driven by escalating global commodity prices, severe supply chain disruptions, and domestic economic instability. This period saw significant financial strain on households, with the cost of essentials such as food and fuel soaring.
August 2022: The Pakistani government, led by Prime Minister Shahbaz Sharif, implemented emergency measures to combat inflation. These measures included the introduction of subsidies for essential goods and a series of economic reforms aimed at stabilizing the economy. Finance Minister Miftah Ismail highlighted the urgency of these interventions to prevent further economic decline.
December 2022: The State Bank of Pakistan (SBP), under the leadership of Governor Jameel Ahmad, raised interest rates to curb inflation. The central bank’s policy included several rate hikes intended to stabilize the currency and control rising prices. This aggressive monetary policy aimed to cool down the overheating economy and restore investor confidence.
April 2023: In response to continued inflationary pressures, the Pakistani government unveiled additional fiscal measures. These included comprehensive tax reforms and increased subsidies for low-income families. The objective was to reduce the financial burden on consumers and stimulate economic growth.
January 2024: Preliminary signs of economic stabilization emerged as global commodity prices began to stabilize and domestic supply chains improved. Dr. Aisha Farooqi, Chief Economist at the Pakistan Institute of Development Economics, noted that the inflation rate could potentially decrease further if current trends persisted.
February 2024: The inflation rate fell to 23.1%, reflecting the combined effects of previous economic measures and favorable external conditions. This decline was attributed to improved supply chain logistics, stabilization of global commodity prices, and effective domestic policies.
Expert Opinions
Dr. Aisha Farooqi, Chief Economist at the Pakistan Institute of Development Economics, commented, “The reduction in inflation to 23.1% is a significant achievement. It underscores the effectiveness of recent fiscal and monetary policies. The challenge now is to maintain this momentum through continued reform and strategic economic planning.”
Mohammad Ali Shah, Financial Analyst at Standard Chartered Bank, observed, “The drop in inflation indicates positive progress. However, it is essential to continue monitoring global economic conditions and domestic fiscal policies to ensure long-term stability and prevent potential setbacks.”
Sara Khan, Economic Advisor with the World Bank, stated, “Pakistan’s progress in reducing inflation is commendable. The country must remain vigilant against external economic shocks and persist in implementing sound economic policies to sustain this positive trend.”
Ali Ahmed, Senior Economist at the International Monetary Fund (IMF), added, “The reduction in inflation reflects the initial success of Pakistan’s economic reforms. Continued focus on structural reforms and fiscal discipline will be crucial to achieving sustained economic growth.”
Economic Implications
Consumer Impact: The slowdown in inflation has provided much-needed relief to Pakistani consumers. Lower inflation rates have led to reduced prices for essential goods, enhancing purchasing power and improving living standards.
Business Environment: A more stable inflation rate contributes to a predictable business environment. Reduced cost volatility benefits companies by providing a more stable foundation for investment and planning, which can stimulate economic growth and job creation.
Government Policies: The successful reduction in inflation validates the recent economic policies implemented by the Pakistani government. Ongoing commitment to fiscal responsibility and monetary stability will be vital for maintaining this positive trend and addressing future economic challenges.
Global Market Effects: Pakistan’s improved inflation rate may influence regional economic dynamics. A stable inflation environment can boost investor confidence and attract foreign investment, supporting broader economic development in the region.
Additional Context and Details
Fiscal Measures: The Pakistani government’s fiscal measures, including targeted subsidies and tax reforms, played a crucial role in managing inflation. These measures were designed to mitigate the impact on low-income households and support economic recovery.
Monetary Policy: The SBP’s monetary policy, including interest rate hikes, was aimed at controlling inflation and stabilizing the currency. This approach was essential in addressing the overheating economy and restoring market confidence.
Global Commodity Prices: The stabilization of global commodity prices, such as oil and food products, contributed to the decline in inflation. Fluctuations in global markets have a direct impact on domestic inflation rates, and recent stabilization has been favorable for Pakistan.
Supply Chain Improvements: Enhanced efficiency in domestic supply chains helped reduce the cost of goods. Improvements in logistics and transportation played a key role in alleviating inflationary pressures.
External Sources
- World Bank – Pakistan Economic Update
- Pakistan Institute of Development Economics – Inflation Reports
- Standard Chartered Bank – Market Analysis
- International Monetary Fund – Pakistan Economic Outlook
Conclusion
Pakistan’s achievement of a 23.1% inflation rate in February 2024 represents a significant economic milestone. This decline reflects the success of recent policy measures and provides a more stable environment for consumers and businesses. Continued economic reforms and vigilant policy adjustments will be crucial for sustaining this positive trend and addressing future economic challenges.
For Regular News and Updates follow – Daily Business
FAQs
1. What were the primary factors leading to the decline in Pakistan’s inflation rate in February 2024?
The primary factors include improved supply chain logistics, stabilization of global commodity prices, and effective domestic fiscal and monetary policies implemented by the government.
2. How has the reduction in inflation impacted Pakistani consumers?
The reduction in inflation has led to lower prices for essential goods, enhancing consumers’ purchasing power and improving their overall standard of living.
3. What measures did the Pakistani government implement to manage inflation?
The government introduced subsidies for essential goods, implemented tax reforms, and adjusted monetary policies, including raising interest rates, to stabilize the economy and reduce inflation.
4. What are the long-term economic implications of the current inflation rate for Pakistan?
Long-term implications include increased economic stability, improved investor confidence, and potential growth in foreign investment. Continued economic reforms and fiscal discipline will be essential for maintaining these benefits.
5. How do global economic conditions affect Pakistan’s inflation rate?
Global economic conditions, such as fluctuations in commodity prices and international trade dynamics, directly impact Pakistan’s inflation rate. The country must adapt its policies to mitigate these external pressures and maintain economic stability.